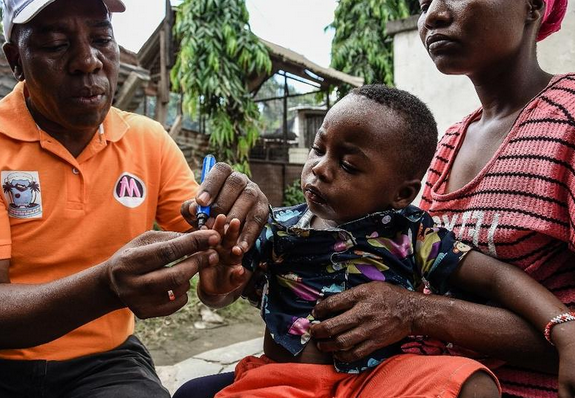
Quality altering mosquitoes so they kick the bucket before intestinal sickness parasites can foster inside them could stop the spread of the destructive parasite completely, as per lab review and PC models
Jungle fever conveying mosquitoes have been hereditarily changed in a manner that eases back the improvement of any jungle fever parasites inside them and furthermore decreases the life expectancy of the mosquitoes. The outcome is that the changed bugs kick the bucket before they can spread the illness.
Lab studies and PC models recommend this could totally stop the spread of the lethal parasite, says colleague George Christophides at Magnificent School London.
“The mix of the two will take out intestinal sickness transmission,” he says.
For the way to deal with work, something many refer to as a quality drive would need to be utilized to spread the necessary hereditary change all through wild mosquito populaces. This is a component that prompts a particular piece of DNA being acquired by all posterity, instead of only half as normally occurs. The quality drive makes that piece of DNA spread in a populace regardless of whether it is disadvantageous.
No designed quality drive has yet been utilized in the wild – albeit normally happening variants exist – however CRISPR-based quality drives have been effectively tried in confined mosquitoes.
Scientists in Tanzania are currently modifying neighborhood mosquitoes similarly as the analysts in London to perceive how well the change neutralizes nearby jungle fever parasites. On the off chance that these examinations are a triumph, the groups desire to team up on field preliminaries in Tanzania, however for the time being the work is bound to labs.
“We are not delivering anything,” says Christophides.
The new work depends on the way that it requires somewhere in the range of 10 and 12 days for jungle fever parasites to foster inside a mosquito and arrive at its salivary organs. Just by then can mosquito chomps taint individuals, yet in the wild Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes, which can convey jungle fever, ordinarily live for only 10 days.
“So you can crash the whole transmission cycle by deferring parasite improvement,” says Christophides
To do this, his group hereditarily changed A. gambiae mosquitoes so cells in their guts emit two little proteins recently displayed to defer parasite improvement. One of these proteins comes from the African tore frog, the other from bumble bees.
At the point when the changed mosquitoes are contaminated, it requires a couple of days longer before malarial parasites can be distinguished in the tops of the mosquitoes, the group has shown. Likewise, the change likewise abbreviates the existences of mosquitoes by several days, says Christophides, further decreasing the possibilities of any mosquitoes sufficiently enduring to become irresistible.
Understand more: Almost 33% of nibbles by jungle fever conveying mosquitoes are in the day
There are two expected issues with the methodology. As a quality drive spreads the change, there would be a gamble of malarial parasites developing protection from the two proteins. To stay away from this, spreading the change among mosquitoes however much as could be expected, says Christophides will be significant. The quicker a parasite populace implodes, the lower the chances of obstruction developing.
It is likewise conceivable that mosquitoes develop such that stops the quality drive working. The quality drive would be intended to limit this gamble, says Christophides.
Different gatherings are dealing with quality drives intended to clear out mosquito populaces, for example by making all female posterity barren while guys stay prolific and keep spreading the quality drive.
These two methodologies might actually be utilized together. For example, a stellar drive could be utilized to clear out mosquitoes in a locale and afterward any that get by or rolled in from one more region could be changed by one more drive to forestall them spreading jungle fever.
“We accept that the two of them can contribute,” says Christophides.
In Brazil, a great many hereditarily changed male mosquitoes are as of now being delivered to decrease wild mosquito numbers. These GM mosquitoes convey a quality that kills the posterity of any female mosquitoes they mate with. There is no proof that this quality endures in nature.